According to the majority of people, the loss of teeth is caused only by accidents or poor dental treatment. As a matter of fact, there are people born without some teeth because of a condition called hypodontia. The condition afflicts a greater number of children and adults than what most people are aware of.
Being informed about Hypodontia in Orthodontics and getting the right type of care will make your smile beautiful, your teeth work better, and your self-esteem and self-confidence soar.
What is Hypodontia in Orthodontics?
Hypodontia is a health condition of the mouth where an individual is born with one or more missing teeth. It does not occur as a result of loss of teeth to decay or injury; instead, the teeth do not develop in the first place. This usually happens at the most infantile phase of tooth formation, usually before the time of birth.
In hypodontia the most commonly affected teeth are
- Upper lateral incisors
- Second molars
- Lower central incisors
Important issues to note:
- Hypodontia is not caused by poor oral hygiene but is a genetic problem.
- It attacks permanent and not primary (baby) teeth.
- Treatment is intended to heal functionality and beauty.
- Diagnosis will enhance treatment outcomes.
Understanding Hypodontia vs. Oligodontia
People often get confused about the difference between these two conditions. While they’re related, the number of missing teeth determines the diagnosis.
| Condition | Definition | Severity |
| Hypodontia | Missing 1–6 teeth | Mild to moderate |
| Oligodontia | Missing 6 or more teeth | Severe, often linked with syndromes |
Hypodontia Causes and Genetics
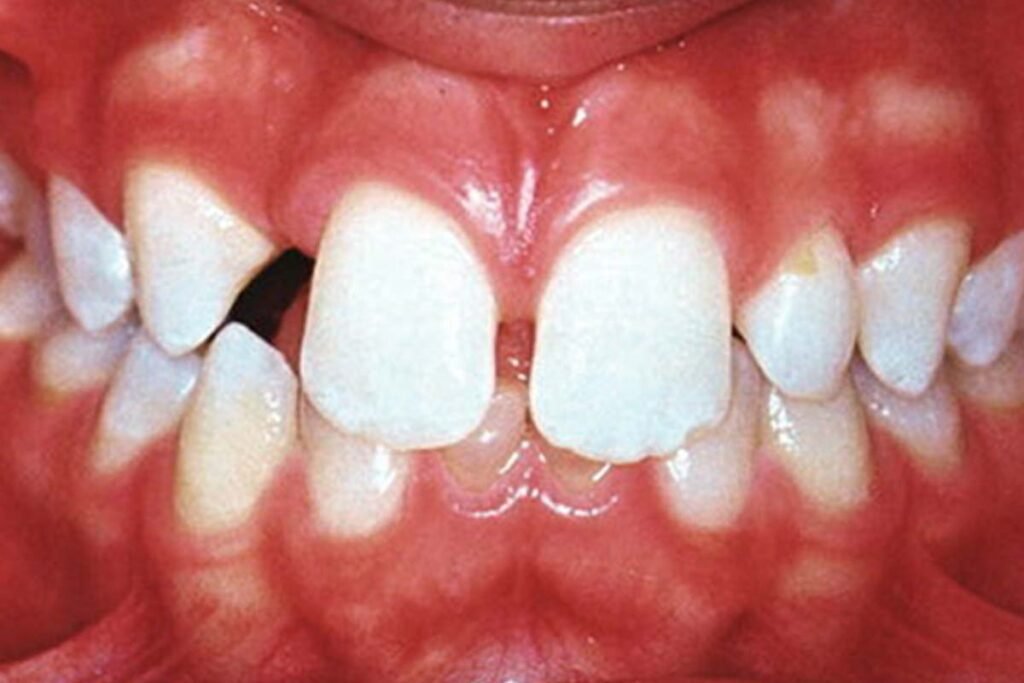
The most important factor is the genetics of hypodontia. Research indicates that children are at increased risk in case one of their parents has the condition. The trait is hereditary, but the mode of inheritance is different.
Scientists have discovered that there are a number of genes necessary in developing the teeth. In case of malfunctioning of these genes, teeth are likely to develop abnormally. The MSX1, PAX9, and AXIN2 are the most frequently associated genes with hypodontia. Learn more about the genetic causes of hypodontia from this detailed research article by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
The main causes of hypodontia may exist other than genetics:
- Pregnant women who get exposed to environmental influences like some infections or drugs.
- Radiation or chemotherapy in childhood.
- Developmental deformities that involve tooth buds.
- Jaw trauma in early childhood.
Hypodontia-Associated Syndromes
Hypodontia is sometimes a component of a bigger genetic disorder. In the case of oligodontia, where many of the teeth are missing, physicians usually seek other indications that could be symptoms of a syndrome.
Missing teeth commonly cause some syndromes, including:
- Ectodermal Dysplasia– It involves the skin, hair, nails, and teeth. Individuals can possess very few teeth, sparse hair and reduced sweating.
- Down Syndrome- The children tend to lack or develop teeth slowly.
- Cleft Lip and Palate- The cleft conditions usually have missing teeth, especially the lateral incisors.
- Rieger Syndrome – It Involves the development of the eyes, the face, and teeth.
Hypodontia and Infertility: Is There a Connection?
Other patients inquire about hypodontia and infertility following the exposure to the potential relationships. This is because some studies have been done on certain genetic mutations. In some studies, it has been found that certain mutations in genes, mostly in the WNT10A gene, are associated with missing teeth in addition to reproductive problems. Nevertheless, one should know that:
- Not all individuals with hypodontia are infertile.
- The relationship is under investigation.
- The majority of individuals who lose their teeth are reproductively healthy.
Signs Your Child May Need Hypodontia Orthodontic Treatment
The most common question that parents pose is, “How do I know whether my child has hypodontia?” The treatment planning is made easy by early detection.
The following are signs to be noted:
- Unfallen-out baby teeth at the age of expectation.
- Huge interdental spaces that appear abnormal.
- Late permanent tooth eruptions.
- One side of the mouth is growing asymmetrically, unlike the other.
- A strange narrow or tiny jaw.
- Inability to chew or articulate words well.
Dentists normally use x-rays when a person is between six and seven years old to know what permanent teeth have been formed. It is at this stage that hypodontia is normally determined. The sooner it is detected, the greater the treatment possibilities and the better the outcome.
Benefits of Early Hypodontia Treatment
Hypodontia orthodontic treatment at the appropriate moment has numerous benefits, which are not limited to sealing gaps.
Correct development of the jaw: In case of the absence of the teeth, the jaw may fail to grow up to its full volume. Expanders, or space maintainers, used at an early age are used to lead to proper growth.
Enhanced bite efficiency: Missing teeth may lead to lateral relocation of other teeth, thus resulting in bite problems. These complications are avoided through treatment.
Better speech: The absence of some teeth, in particular, front teeth, influences the pronunciation of some sounds among children. The replacement or planning of these teeth contributes to the development of speech.
Prevents shifting: In the case of a gap, the neighboring teeth will drift to fill this gap and complicate future treatment.
If your child needs orthodontic care, it’s smart to plan early. Discover helpful tips in our article Back to School: Plan Your Braces Before School Opens for a smooth and confident start.
Treatment Approaches for Hypodontia / Missing teeth
What is the treatment of orthodontists regarding hypodontia? The strategy will be based on the number of missing teeth, the age of the patient, and the missing teeth. No single solution fits all, but the following are the key ones:
- Space closure using braces—it is a technique of closing the gap. The neighboring teeth are slowly pushed by the braces such that the gap created by the lost tooth fades.
- Space maintenance- Braces assist in maintaining the appropriate space for future implants. As soon as the growth of jaws ceases, an implant may be inserted into that gap. Sometimes a baby tooth may be retained for as long as possible in occlusion.
- Dental implants—Implants are used after growth has ceased which is normally in the late teens or early twenties, and the missing teeth are replaced by implants. They resemble and act like natural ones.
- Bridges—A bridge involves a bridge that is connected to the adjacent teeth to support a replacement. It is a good alternative in case implants cannot be used.
- Composite bonding—by minimally expanding neighboring teeth with tooth-like substance, one can bridge minimal gaps and enhance beauty.
- Combination approaches—most patients benefit by being treated using multiple methods simultaneously as they develop.
For patients using clear aligners during their hypodontia treatment, maintaining proper hygiene is crucial. Learn how to clean Invisalign and retainer trays the right way to keep your orthodontic appliances fresh and bacteria-free.
Why Choose Specialized Orthodontic Care for Hypodontia

Treating hypodontia requires more than simply straightening teeth. It desires a complete technique that considers boom, function, aesthetics, and long-term stability.
When you work with an experienced orthodontist, you get:
- Complete diagnosis through the use of advanced imaging like three- 3D scans
- Coordinated care with other specialists, like oral surgeons and prosthodontists
- A customized remedy plan that evolves as you grow
- Monitoring at some stage in the improvement to regulate the plan as needed
- Focus on each characteristic and appearance.
At Art of Smile, we also use cutting-edge tools like 3D imaging and virtual modeling to ensure precision in every case. Explore how 3D printing and virtual treatment planning are shaping the future of orthodontics.
Key Takeaways for Hypodontia in Orthodontics
| Focus Area | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Early Diagnosis | Helps plan space and prevent bite issues |
| Customized Treatment | Tailored orthodontic and restorative care |
| Genetic Awareness | Family history helps predict and prevent |
| Cost Flexibility | Affordable options for every patient |
| Comprehensive Care | A team approach ensures full smile restoration |
Final Thoughts
Hypodontia orthodontic remedy has come a long way. What was once regarded as an insurmountable venture now has many effective answers. It’s not just about filling gaps in your smile. It’s about ensuring proper jaw development, maintaining excellent bite function, and giving patients the confidence that comes with a complete, healthy smile.
The secret is early diagnosis and making comprehensive remedy plans. Whether via area closure, implants, or mixture processes, cutting-edge orthodontics gives first-rate results for patients with hypodontia.
If you or your toddler child lacks permanent enamel, schedule a consultation with Dr. Kanchi Shah, BDS, DDS, an orthodontist who specializes in hypodontia at Art of Smile. She will help you create a custom-designed plan that addresses every on-the-spot need of the patient and let them achieve long-term dreams.
FAQs
Is hypodontia just a cosmetic concern?
No. While appearance matters, hypodontia also affects chewing characteristics, speech development, and jawbone. Treatment addresses some of these purposeful aspects, not just how enamel looks.
What is the best age to start hypodontia treatment?
Early evaluation round at age 6-7 is ideal. However, the exceptional time to begin active remedy relies upon which enamel is lacking and what remedy method is planned. Your orthodontist will endorse the surest timing for your precise case.
Can hypodontia treatment help with other dental problems?
Yes. Comprehensive hypodontia treatment regularly improves chunk alignment, reduces crowding in different areas, and promotes better jaw development. These benefits expand past simply replacing the missing teeth.
How is hypodontia treatment different from regular braces?
Regular braces focus on straightening existing enamel. Hypodontia orthodontic treatment additionally involves strategically making plans for the lacking tooth, whether it means closing areas, keeping areas for future implants, or coordinating with other dental specialists for complete care.